HIIT Conditioning: HIIT Drills – Part 1
In the first part, What You Need To Know, I have presented the basics, as well as the introduction to the High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT). I have also talked mostly about HIIT Prescription. In the following two parts, the emphasis is on HIIT Drills.
I will talk about their classifications and then cover each of these categories in more details. Namely, in this part, I will focus on the first two categories – Long Intervals and Short Intervals, whereas in the next part, other three categories will be covered: Sprint Interval Training (SIT), Repeat Sprint Training (RST) and Intermittent Recovery.
Here is the classification of HIIT drills used in this article series:
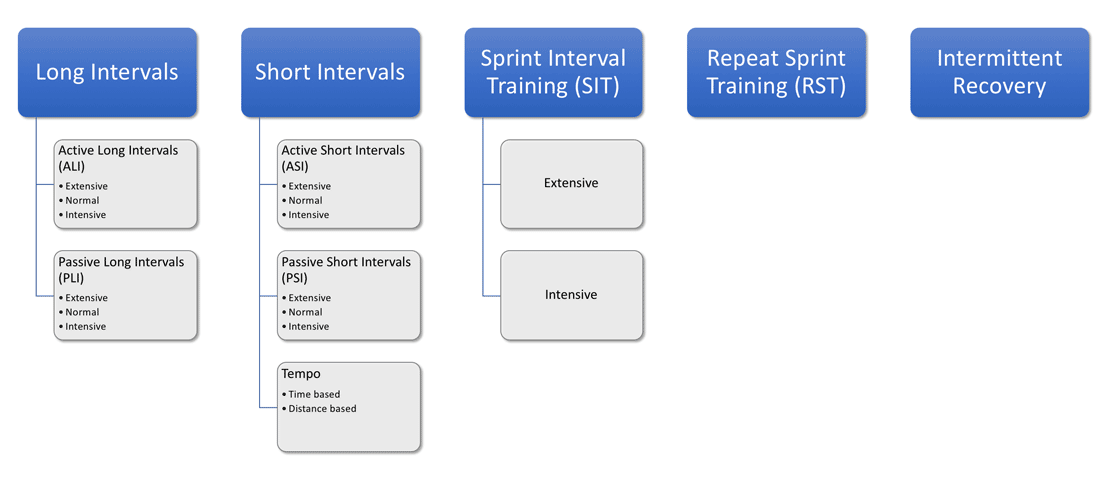
Each of these will be covered in more details, but for the sake of the big picture view, here is Velocity Profile for the Athlete A (MAS 4.44 m/s, MSS 9 m/s), with distribution of HIIT Drills (right side):
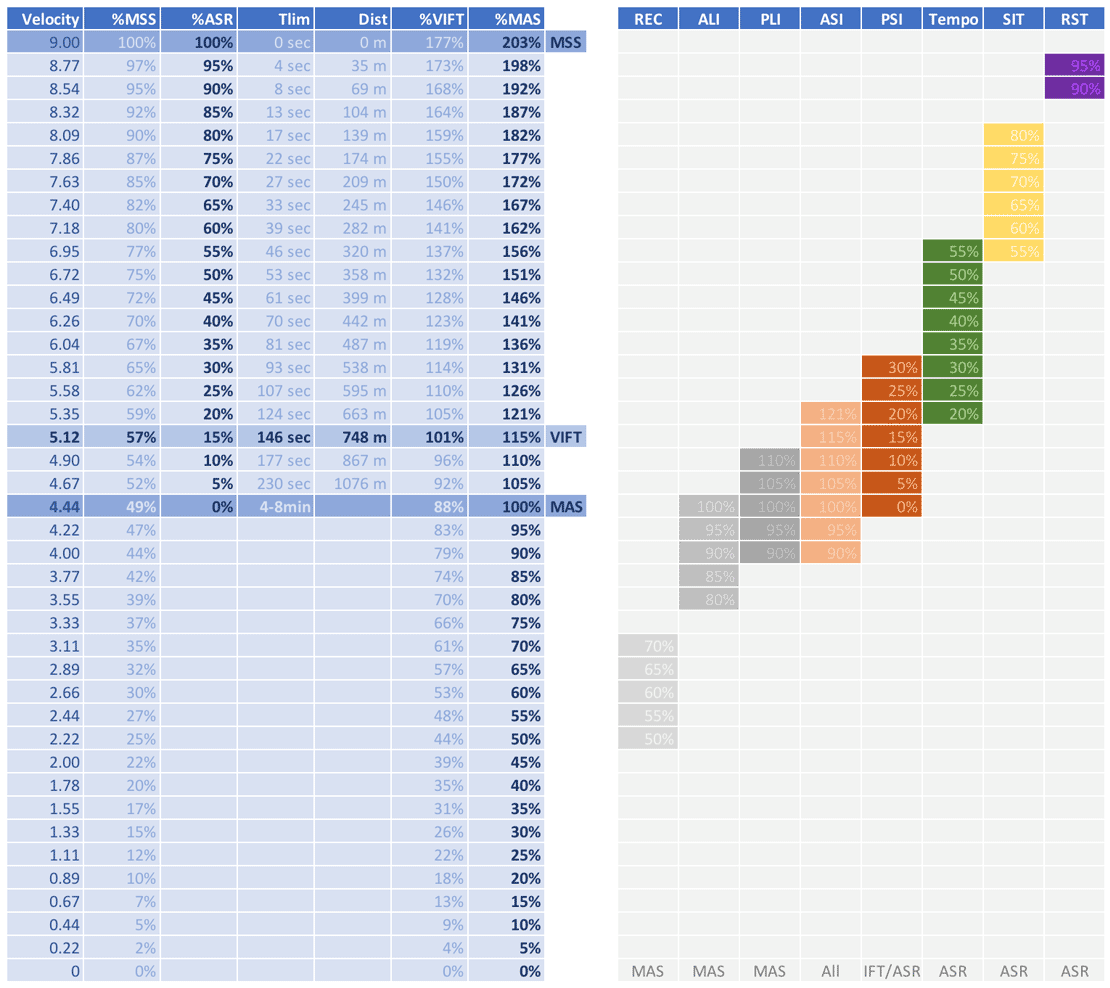
Here, REC stands for recovery interval, performed in active variations of HIT drills, which is around 50-70% MAS.
These two images give a big picture of HIIT drills. Let’s now cover each category in more detail.
Long Intervals
Long intervals are intervals longer that 1 min, usually performed from 80% MAS to 110% MAS. In this book we differentiate between the two variations: long intervals with active rest (ALI) and long intervals with passive rest (PLI).
Since long intervals are, well long, coaches prefer to prescribe them using distance. As explained previously, prescribing in distance is fine when working with a rather small number of athletes, but with the big group, if they run on 800m with their individual times and individual recovery time, it can become quite messy and chaotic.
The solution for these longer intervals would be to prescribe them in shuttles.
Let’s take again the Athlete A with MAS of 4.44 m/s (16 km/h) and MSS of 9 m/s (32.4 km/h) and prescribe passive long intervals (PLI) of 3 minutes work at 100% MAS with 6-minute passive rest. The distance that needs to be covered in those 3 minutes is 800m. That would be easily done if our Athlete A is training alone. But he has 30 more training mates, and the coach decides to organize them in 10 shuttles of 77 meters (corrected for 0.7s COD loss), with a beep in 18 seconds (one shuttle needs to be covered in 18 seconds, which is equal to 180sec / 10 shuttles). This is all easily calculated in the HIT Builder.
Let’s deal with the differences between passive (PLI) and active (ALI) long intervals.
Passive Long Intervals (PLI)
Passive long intervals have a passive break between intervals. During that break athletes can stand or walk. Usually they talk. This passive break affords slightly higher intensity (expressed in % MAS) compared to active break long intervals (see the Long Intervals table).
In this article series, I differentiate between intensive, normal, and extensive variations, which involve 1:2, 1:1, and 2:1 work-to-rest ratios. The following graph will convey the message, as well as the long intervals table.
Active Long Intervals (ALI)
Active long intervals involve active recovery period, in which athlete needs to (in this case) run at 50-70% MAS. To be completely honest, this is always tricky with team sport athletes (in general, but with active long intervals in particular) and much easier to convey with T&F athletes. One solution, with long intervals, are performed in shuttle would be to cover the same distance in double time (with intensive variations, with 1:2 ratio), cover half the shuttles in the same time (with normal variations, with 1:1 ratio), or cover 1/4 shuttles in half the time (with extensive variations, with 2:1 ratio).
Taking the Athlete A (MAS 4.44 m/s, MSS 9 m/s) as an example again. Prescribing active long interval of 2 minutes at 90% MAS, with 2 minutes at 55-65% MAS, in 8 shuttles, the Athlete A will need to cover 8x57m (480m total). During the 2 minutes break, he would need to cover 4x57m, which is not exactly 55-65% (rather 45% MAS), but much easier to organize and perform. If you want to be lab coat and nitpick, go ahead and measure the exact distance. Or just do one more shuttle, 5x57m in 2minutes. Problem solved.
As with passive long interval, here I differentiate between three variants: intensive (1:2), normal (1:1), and extensive (2:1). They are depicted on the image below, but also consult the long intervals table.
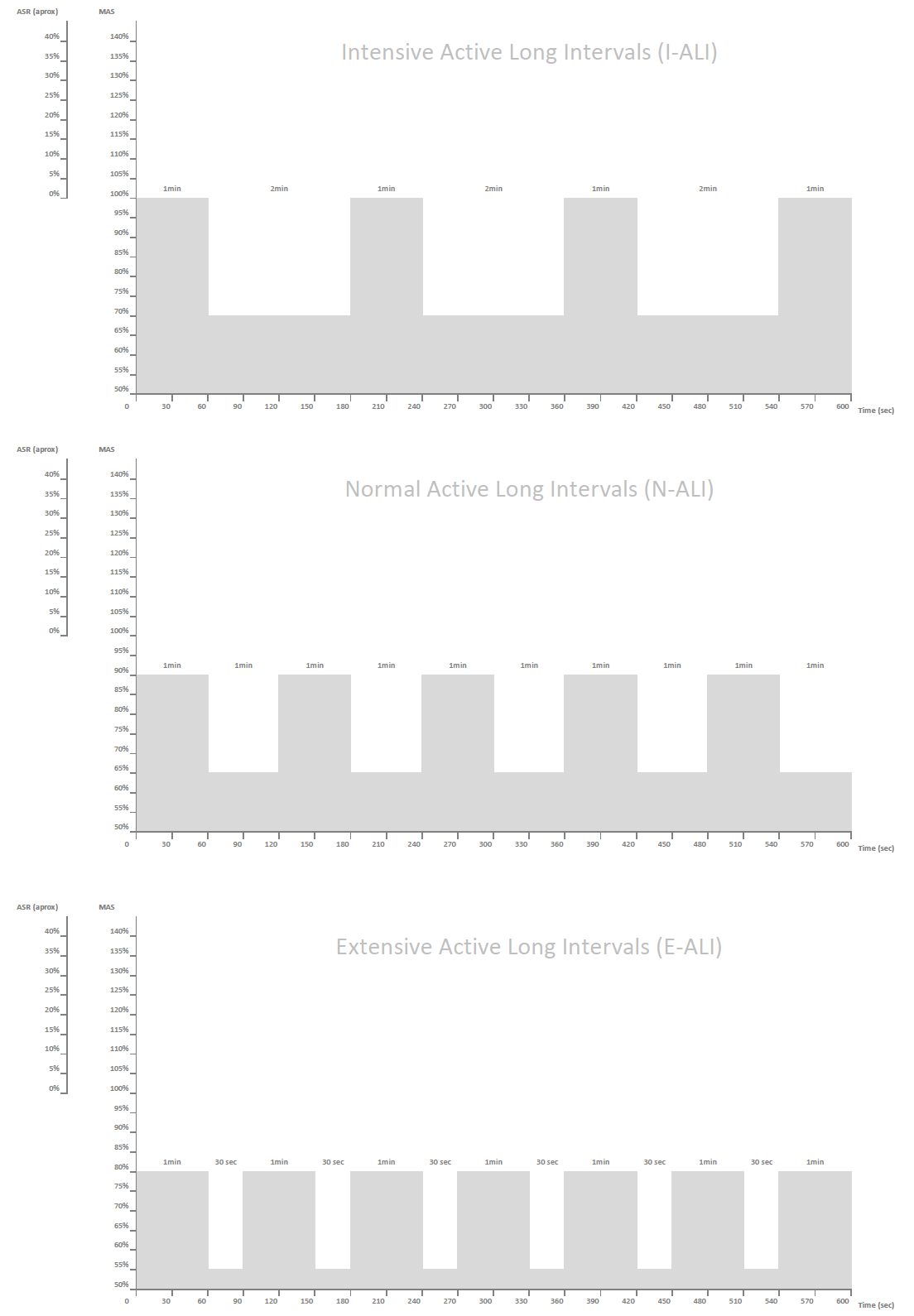
Long Intervals format
One set in the long intervals should be longer than 20-30minutes (e.g. long intervals 3′-3′ takes 6minutes for one repetition, so doing 4x3min is already 24minutes long set). For this reason, long intervals are usually performed for one set only (two tops). In team sports, athletes are already time-constrained, and for that sole reason, long intervals are usually not that frequently performed. They are most likely to be performed when there are not many sport practices (as in the offseason), when the athlete is in the rehab phase, or when the athlete is really shitty with his MAS score (coaching wisdom suggest that lower-level athletes should spend more time with longer intervals). I am an advocate of performing them occasionally through the season, for the sake of variety and covering more ‘extensive’ ranges of conditioning, every now and then. More about this in the upcoming chapter on planning.
Progressions with Long Intervals
First of all, what is progression? In plain English, progression is making things harder (under the same variation). HIIT has a lot of variables to be manipulated, in order to make intervals harder. Here are a few heuristics you can play with (in this particular order):











Responses